The Role of Simulation in Nursing Education
May 22, 2023
Simulation in nursing education has become an increasingly valuable teaching tool. Not only do simulations allow students to problem-solve and apply clinical knowledge in a safe, low-stress environment, but simulated learning modules also allow students to practice what they’ve learned without needing to worry about making mistakes that could harm patients.
From virtual and online environments to hands-on learning with full-body, computer-controlled mannequins, opportunities for simulation-based training are as vast as they are beneficial.
Professionals interested in learning about how to teach the next generation of nurses in virtual and simulated environments should start by developing the knowledge needed to become a nurse educator. An advanced nursing degree with a concentration in nurse education can prepare graduates with the necessary skills to shape the future of nursing.
What Is Simulation in Nursing Education?
Simulations provide students with learning opportunities that extend beyond traditional classroom instruction. For example, unlike hands-on learning in a clinical environment, where nursing students may only encounter patients with a limited number of medical issues, virtual simulations are designed to mimic a wide variety of simple and complex clinical situations.
In addition to increasing variabilities in training, virtual learning environments ensure that real patients aren’t exposed to unnecessary risks.
Common Types of Nurse Simulation Training
Today’s nursing students are frequently exposed to a wide array of scenarios in nurse simulation training. The most common types of nurse educator tools include the following:
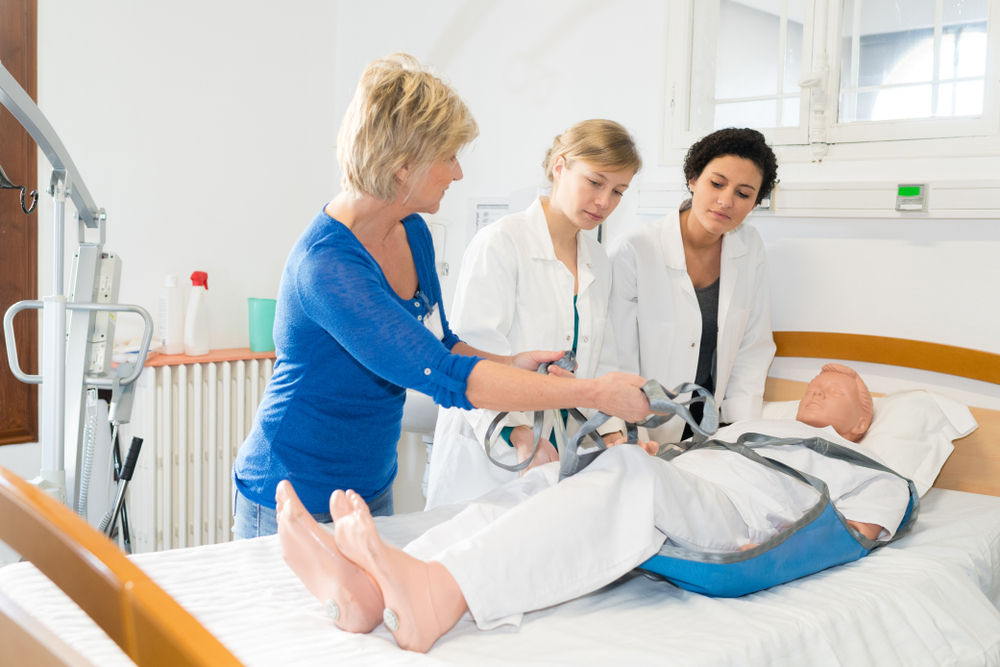
High-Fidelity Mannequins
High-fidelity mannequins are full-body lifelike mannequins designed to physiologically respond as if they were real-life patients. They have heart sounds and pulses and can mimic other bodily functions. These mannequins can help students provide intravenous infusions and detect changes in patients’ conditions.
Low-Fidelity Mannequins
Unlike high-fidelity mannequins that appear quite lifelike, low-fidelity mannequins are less realistic and are used to help students practice basic skills. For example, CPR certification courses use Resusci Anne, a silicone mannequin that consists of a head and torso, to teach students how to open patients’ airways and perform chest compressions.
Partial-Task Simulators
Partial-task simulators are lifelike models of specific parts of anatomy such as the arm, leg or torso, designed to help students gain proficiency in a specific skill. Partial-task simulators can teach students how to draw blood, insert an IV tube or a hep-lock and perform the Heimlich maneuver, among other crucial tasks.
Role-Playing
In role-playing simulations, students take turns assuming the role of a patient or a health care provider. This type of experiential learning allows students to act out various scenarios and use their critical thinking skills. It also requires students to closely examine complex and in some cases controversial medical scenarios and apply their knowledge to solve specific problems.
E-Learning
E-learning modules allow students to participate in computer simulations from anywhere they have access to an internet connection. These simulations can teach students how to use specific pieces of medical equipment or provide virtual patient care simulations designed to help students improve their competency.
Volunteer Patients
In this type of simulation, patients volunteer to help students practice various skills, such as asking for informed consent, asking for a patient to provide their medical history and explaining what patients can expect during a particular procedure. Volunteer patients are also used to help nursing students refine nursing soft skills.
Benefits of Simulation in Nursing Education
A 2021 study in Acta Informatica Medica found that nursing students who participated in simulation in nursing education to practice their decision-making and clinical skills in a protected environment had an enhanced sense of security, which in turn, improved their confidence and self-esteem. The study also found that the further development of simulation-based learning tools can “significantly help the efforts made by students to become integrated and successful healthcare professionals.”
The National Council of State Boards of Nursing agrees that simulation training for nursing students is highly beneficial. Examples of some of the benefits of simulation in nurse education include the following:
- They help students develop clinical reasoning capabilities.
- Simulations train students to become adept in providing care to patients and their families.
- Students are provided with immediate feedback and an opportunity to try again if needed.
- Virtual and mannequin-based simulations can be manipulated to mimic complex medical situations.
- Unlike traditional, classroom-based study, simulations provide students with experiential learning opportunities.
- Simulations allow learners to practice their skills in a safe, controlled environment in which they can make and learn from mistakes, without needing to worry about affecting patient outcomes.
- Learning modules are designed to become harder as curriculum topics become more complex.
Earn Your MSN to Teach the Next Generation of Nurses
Professionals interested in pursuing their passion for educating future nurses must begin with a comprehensive understanding of how to develop lesson plans that encourage professional development. The online Master of Science in Nursing with a Nurse Educator concentration from Walsh University is designed to prepare graduates to teach in a variety of in-person and virtual settings.
Are you ready to take the next step toward becoming a nurse educator? Discover how the online Master of Science in Nursing, Nurse Educator program at Walsh University can provide you with the teaching strategies to succeed.
Sources:
- Acta Informatica Medica, “Simulation in Clinical Nursing Education”
- Healthy Simulation, Nursing Simulation | About & Resources
- Healthy Simulation, Role-Play: A Healthcare Simulation Strategy for Teaching Problem-Solving, Communication, and
- Self-Awareness
- Healthy Simulation, Simulation in Nursing Education
- NCSBN, Simulation Study
